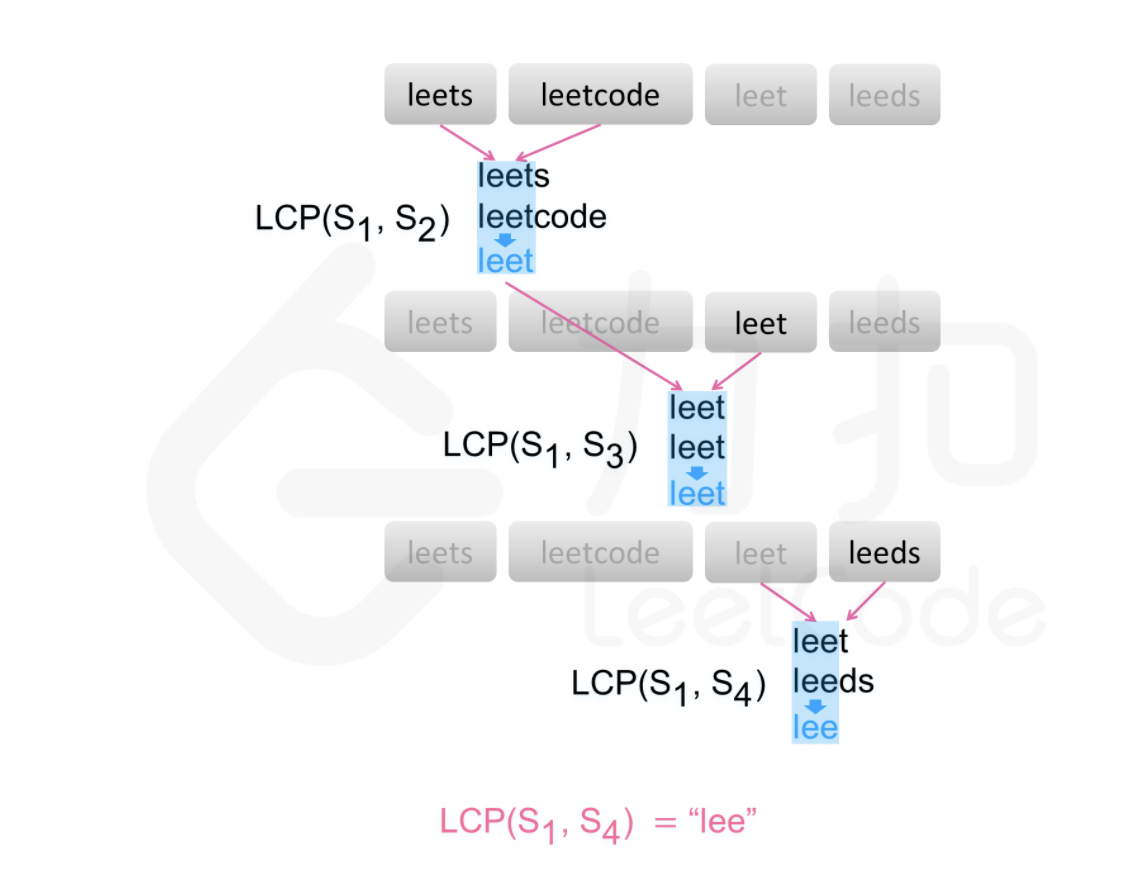
14-最长公共前缀(二分、分治) 法一:横向扫描 用 $LCP(S_1,…,S_n)$ 表示字符串 $S_1,…,S_n$的最长公共前缀,可得
基于该结论可得到一种查找字符串数组中的最长前缀的简单方法。依次遍历字符串中的每个字符串。对于每个遍历到的字符串,更新最长公共前缀,当遍历完所有的字符串以后,即可得到字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。
如果在尚未遍历完所有的字符串时,最长公共前缀已经是空串,则最长公共前缀一定是空串,因此不需要继续遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) if (strs == null || strs.length==0 ){ return "" ; } String prefix = strs[0 ]; int count = strs.length; for (int i = 1 ;i < count;i++){ prefix = longestCommonPrefix(prefix, strs[i]); if (prefix.length() == 0 ){ break ; } } return prefix; } public String longestCommonPrefix (String str1, String str2) int length = Math.min(str1.length(), str2.length()); int index = 0 ; while (index<length && str1.charAt(index) == str2.charAt(index)){ index++; } return str1.substring(0 ,index); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution : def longestCommonPrefix (self, strs: List[str ] ) -> str: if not strs: return "" prifix , count = strs[0 ], len (strs) for i in range (1 ,count): prifix = self.lcp(prifix, strs[i]); if not prifix: break return prifix def lcp (self, str1,str2 ): length, index = min (len (str1), len (str2)), 0 while index < length and str1[index] == str2[index]: index+=1 return str1[:index]
复杂度:
时间$O(mn)$ m是字符串数组中的字符串的平均长度,n是字符串的数量。最坏情况下,字符串数组中的每个字符串的每个字符都会被比较一次。
空间 $O(1)$
法二:纵向扫描 方法一是横向扫描,依次遍历每个字符串,更新最长公共前缀。另一种方法是纵向扫描。
纵向扫描时,从前往后遍历所有字符串的每一列,比较相同列上的字符是否相同。
如果相同则继续对下一列进行比较,如不相同则当前列不再属于公共前缀,当前列之前的部分为最长。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) if (strs==null || strs.length==0 ){ return "" ; } int length = strs[0 ].length(); int count = strs.length; for (int i=0 ;i<length;i++){ char c = strs[0 ].charAt(i); for (int j=1 ;j<count;j++){ if (i==strs[j].length() || strs[j].charAt(i)!=c){ return strs[0 ].substring(0 ,i); } } } return strs[0 ]; } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度 $O(mn)$ 其中 m 是字符串数组中的字符串的平均长度,n是字符串的数量
空间 $O(1)$
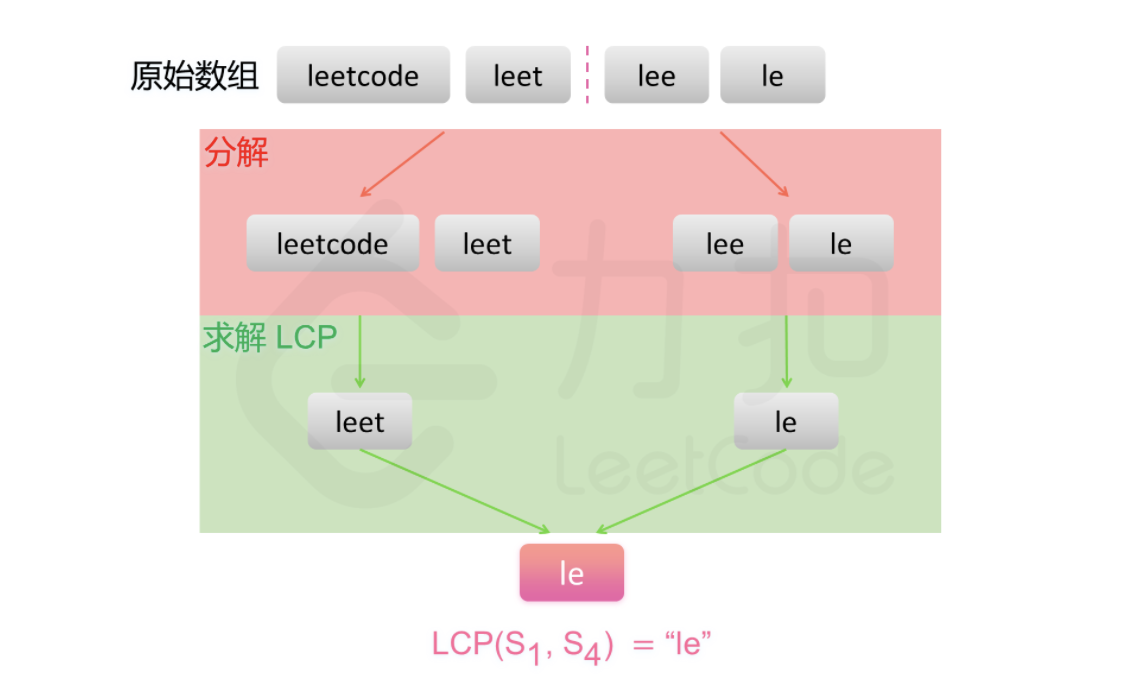
方法三:分治 注意到 LCP 的计算满足结合律,有以下结论:
其中$LCP(S_1,…,S_n)$ 是字符串 $S_1,…,S_n$ 的最长公共前缀,$1<k<n$
基于上述结论,可以使用分治法得到字符串数组中的最长公共前缀。对于问题 $LCP(Si,…,S_j)$,可以分解成两个子问题 $LCP(S_i,…,S {mid})$ 与$LCP(S_{mid+1},…,S_j)$
其中 $mid = \frac{i+j}{2}$ 对两个子问题分别求解,然后对两个子问题的解计算最长公共前缀,即原问题的解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) if (strs==null || strs.length==0 ){ return "" ; } return longestCommonPrefix(strs, 0 , strs.length-1 ); } public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs, int start, int end) if (start == end){ return strs[start]; } int mid = (end - start) / 2 + start; String lcpLeft = longestCommonPrefix(strs, start, mid); String lcpRight = longestCommonPrefix(strs, mid+1 , end); int minLength = Math.min(lcpLeft.length(), lcpRight.length()); for (int i=0 ;i<minLength;i++){ if (lcpLeft.charAt(i) != lcpRight.charAt(i)){ return lcpLeft.substring(0 ,i); } } return lcpLeft.substring(0 ,minLength); } }
时间复杂度:
时间复杂度:$O(mn)$ 其中m 是字符串数组中的字符串的平均长度,n是字符串的数量。
时间复杂度的递推式是 $T(n) = 2\cdot T(n/2) + O(m)$, 通过计算可得 $T(n) = O(mn)$
空间复杂度 $O(mlogn)$ ,n为字符串数量。空间复杂度取决于递归调用的层数,层数最大为 logn,每层需要 m 的空间存储返回结果。
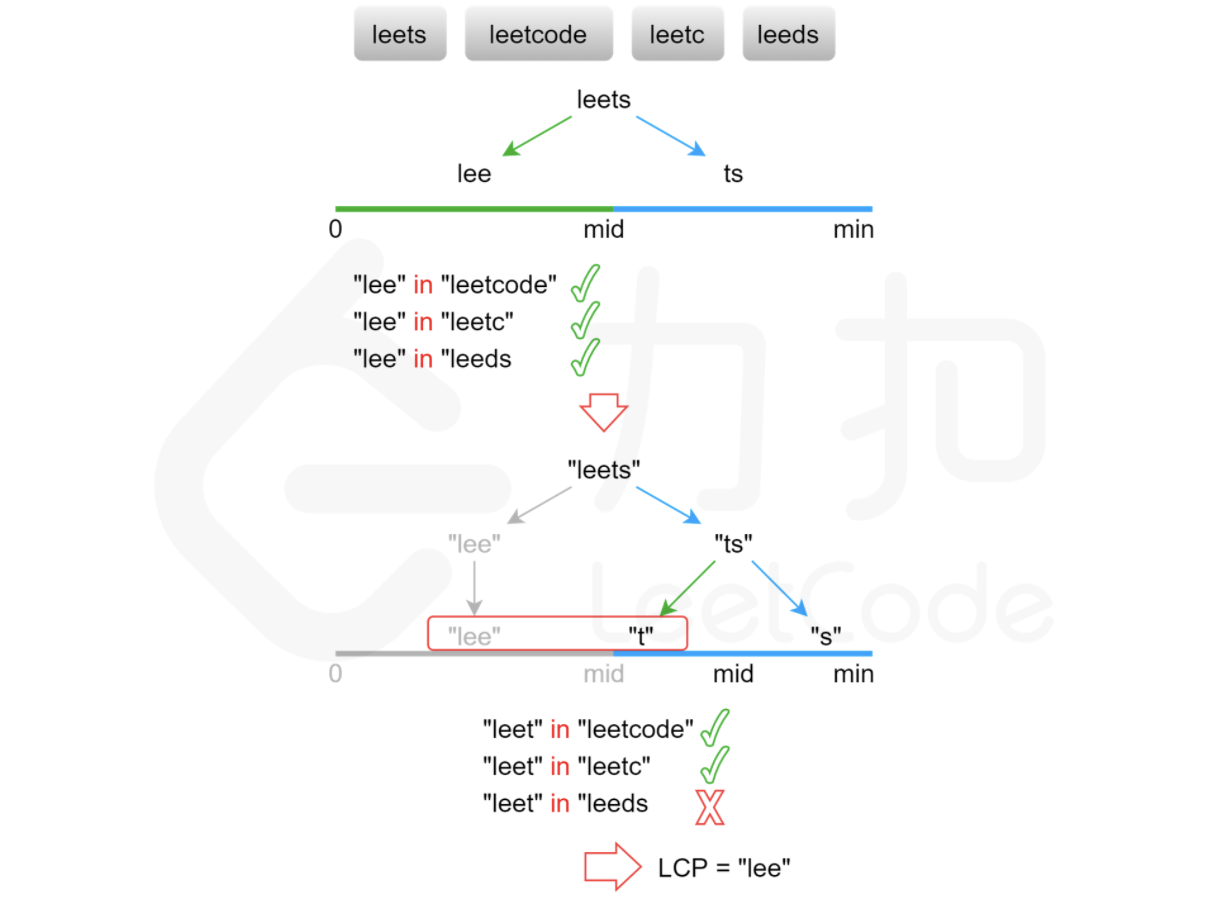
方法四:二分查找 虽然,最长公共前缀的长度不会超过字符串数组中的最短字符串的长度。
用 minLength 表示字符串数组中的最短字符串长度,则可以再 $[0,minLength]$ 的范围内通过二分查找找到最长公共前缀的长度。每次取查找范围的中间值mid, 判断每个字符串的长度为mid 的前缀是否相同,如果相同则最长公共前缀的长度一定大于或等于 mid, 如果不相同则最长公共前缀的长度一定小于mid, 通过上述方式将查找范围缩小一半,直到得到最长公共前缀的长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) if (strs==null || strs.length==0 ){ return "" ; } int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE for (String str:strs){ minLength = Math.min(minLength, str.length()); } int low = 0 , high=minLength; while (low < high){ int mid = (high - low + 1 ) /2 + low; if (isCommonPrefix(strs, mid)){ low = mid; }else { high = mid-1 ; } } return strs[0 ].substring(0 ,low); } public boolean isCommonPrefix (String[] strs, int length) String str0 = strs[0 ].substring(0 , length); int count = strs.length; for (int i=1 ;i<count;i++){ String str = strs[i]; for (int j=0 ;j<length;j++){ if (str0.charAt(j) != str.charAt(j)){ return false ; } } } return true ; } }